Introduction
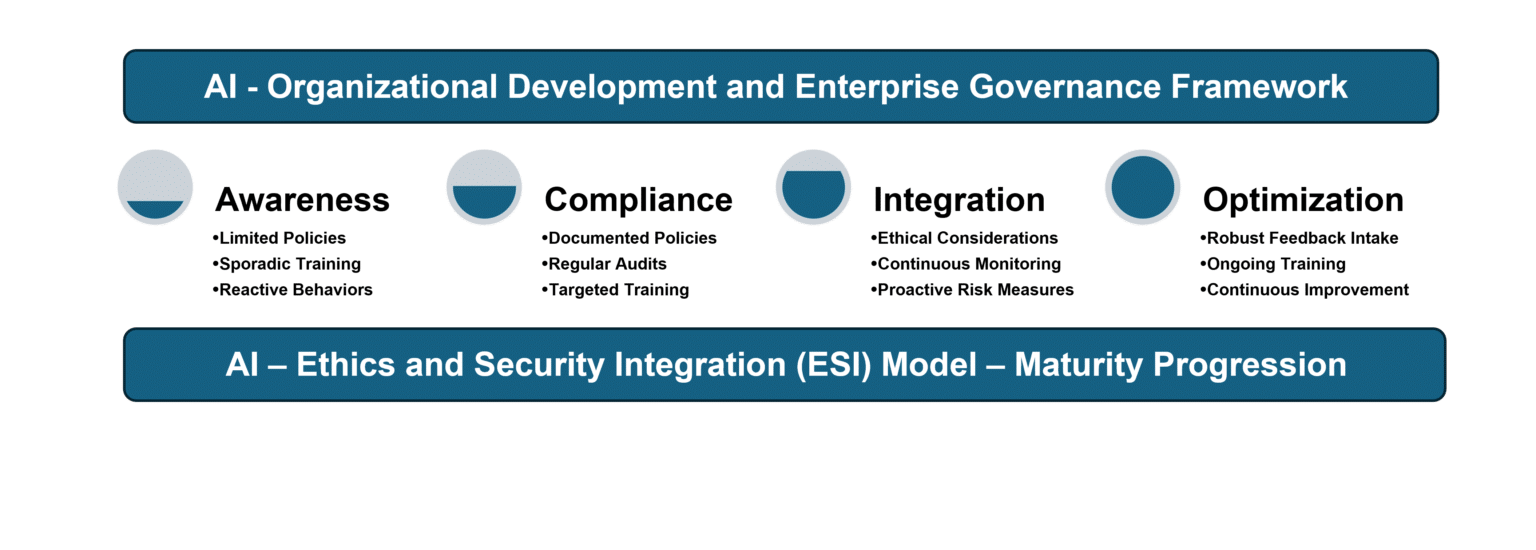
The AMS AI-Organizational Development and Enterprise Governance Framework is a comprehensive solution designed to seamlessly integrate ethical considerations and security measures into your AI system implementation, at the confluence of AI and the human element. Leveraging the Ethical Security Integration (ESI) Model, it ensures a holistic approach, emphasizing the ethical use of AI technologies and enhancing security aligned with your organizational core values. The model focuses on integrating ethical principles throughout AI development, deployment, and operations, promoting responsible and secure practices. By adopting the ESI model and utilizing the supportive AI – Organizational Readiness Assessment businesses can strike a harmonious balance between ethics and security, creating a trustworthy and responsible AI-driven environment. It doesn’t replace existing AI platforms but provides access to best practices, leveraging a proprietary assessment process to identify gaps and measure the progression towards synchronized AI integration across all business functions.
The ESI model is supported by a Maturity Progression that will keep your transformational change on target and allow for clarity across the enterprise during integration.
Embracing the benchmark to gain enhanced ROI
-
Ethical Synergy: A Unified Code of Conduct
In the harmonious confluence of AI and OD, ESI emerges as the guardian of ethical considerations, ensuring that a robust ethical code underpins technological advancements. By integrating ESI into the broader Organizational Development Framework, companies instill a culture that values transparency, fairness, and responsible AI use. This integration goes beyond a mere checklist, making ethical principles an integral part of the organizational DNA and influencing decision-making at every level.
-
Security and Collaborative Excellence: Safeguarding Innovation
ESI, with its unwavering commitment to security, seamlessly aligns with the collaborative spirit championed by organizational development. As companies embrace cross-functional teams and encourage interdepartmental cooperation – integral aspects of the Organizational Development Framework – ESI ensures that collaboration occurs within the secure confines of robust data protection and vigilant threat prevention measures. This dynamic synergy guarantees that ESI's dedication to data security fortifies the collaborative excellence fostered by OD.
-
ESI as an Innovation Catalyst: Where Ethics Meet Ingenuity
Innovation, a central tenet of organizational development, finds a reliable partner in ESI. As organizations strive for continuous improvement and foster a culture that values experimentation, ESI acts as a catalyst, ensuring that innovative endeavors are not only cutting-edge but also ethically sound and secure. This dynamic synergy fosters an environment where AI-driven innovation not only thrives but does so without compromising ethical principles or jeopardizing data security.
-
Learning Culture Driven by ESI: Empowering Minds Ethically
The OD Framework places a premium on continuous learning, and with the integration of ESI, this ethos extends seamlessly into the realm of AI. ESI-driven learning initiatives ensure that employees are not only upskilled for AI-related roles but are also well-versed in the ethical considerations associated with AI technologies. This aligns with the OD principle of empowering the workforce and creating a learning organization poised for the challenges posed by an AI-driven landscape. Employees become not just skilled practitioners of AI but conscientious contributors to an ethical and secure AI environment.
-
Strategic Alignment Enhanced by ESI: Where Goals and Ethics Converge
Strategic alignment, a cornerstone of organizational development, gains added depth with the inclusion of ESI. Companies that seamlessly align AI strategies with broader business goals, a principle championed by OD, find in ESI a guiding framework. ESI ensures that AI initiatives are not only strategically aligned but also ethically and securely executed. This confluence creates an organizational culture where strategy, ethics, and security are interwoven seamlessly, ensuring a holistic approach to AI integration that contributes positively to the organizational objectives.
-
ESI as a Pillar for Organizational Resilience: Building for Tomorrow
The integration of ESI with the Organizational Development Framework creates a powerful synergy that fortifies the organizational culture against the challenges of the AI era. ESI becomes a pillar supporting ethical considerations, enhancing data security, and imbuing the workforce with the skills and mindset needed to thrive in an AI-driven landscape. Together, ESI and OD forge a resilient organizational culture that not only embraces AI but does so with a steadfast commitment to ethics, security, and continuous development. This harmonious confluence positions organizations not just to adapt to change but to lead it with unwavering integrity and foresight. In this collaborative dance of technology, ethics, and development, ESI stands as the guiding partner, ensuring a resilient and future-ready organizational culture.
Conclusion: Envisioning Tangible Triumphs and ROI in the Synergy of AI, Organizational Development, and ESI
In the culmination of our exploration into the harmonious confluence between AI, Organizational Development (OD), and the Ethics and Security Governance Framework (ESI), it becomes crucial to project the expected Return on Investment (ROI) alongside tangible triumphs emerging from this synergistic collaboration.
At the forefront of quantifiable outcomes is the envisaged increase in operational efficiency. By aligning AI strategies with organizational goals through ESI-infused OD, companies can anticipate a streamlined workflow, reduced operational redundancies, and, consequently, a measurable boost in productivity. The ROI here is reflected not only in time saved but also in the enhanced output and efficiency metrics.
The integration of ESI fortifying security measures is a linchpin for ROI. As security incidents decrease due to the proactive security measures advocated by ESI within the collaborative OD environment, organizations stand to gain financially. The potential savings from mitigating financial losses associated with security breaches, coupled with the added value of safeguarding sensitive data, contribute significantly to the ROI equation.
Continuous learning, a cornerstone of ESI, is poised to bring about a measurable rise in employee productivity. As the workforce adapts to AI technologies with ethical considerations and security consciousness, organizations can expect quantifiable improvements in project completion rates, output quality, and overall efficiency. The ROI becomes evident in the increased output and the innovation potential realized through a skilled and adaptable workforce.
The innovative edge gained through the confluence of ESI, AI, and OD sets the stage for ROI in market positioning and growth. Organizations can anticipate measurable returns in the form of successful AI-driven innovations, elevated market positions, and potentially, increased revenue streams. The investment in cutting-edge technological solutions, underpinned by ESI principles, is projected to yield tangible results in terms of market competitiveness.
Employee satisfaction and retention rates serve as another metric for ROI in the collaboration between ESI and OD. The anticipated workplace improvements, characterized by ethical AI use, prioritized employee development, and a secure environment, can lead to quantifiable returns. A satisfied and retained workforce reduces recruitment costs, enhances team stability, and contributes to an organization's overall resilience.
When considering the Return on Investment (ROI) related to the use of the Ethics and Security Governance Framework (ESI) in the integration of AI and Organizational Development, it's important to focus on specific areas influenced by ESI principles. Here's a more tailored approach:
-
Compliance Cost Reduction:
- Evaluate the cost savings achieved through proactive compliance with ethical and security standards.
- Consider the potential financial impact of avoiding legal consequences associated with non-compliance.
- Project ROI based on the reduced expenses related to adherence to regulatory frameworks.
-
Data Breach Avoidance:
- Assess the financial value of preventing data breaches and unauthorized access.
- Consider potential losses avoided by safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining data integrity.
- Project ROI based on the avoided costs of remediation, legal actions, and reputation damage.
-
Trust and Reputation:
- Quantify the impact of enhanced trust and reputation resulting from ethical AI practices.
- Consider the potential financial gains from being perceived as a trustworthy and responsible organization.
- Project ROI based on the positive influence on customer loyalty, brand perception, and stakeholder trust.
-
Security Infrastructure Investment:
- Evaluate the ROI of investments in security infrastructure guided by ESI principles.
- Consider the long-term cost savings from having a robust security foundation.
- Project ROI based on the efficiency and effectiveness of security measures implemented.
-
Employee Morale and Productivity:
- Assess the financial impact of improved employee morale and job satisfaction.
- Consider potential cost savings related to increased productivity and reduced absenteeism.
- Project ROI based on the positive influence of ESI on the overall well-being and engagement of the workforce.
-
Risk Mitigation:
- Evaluate the financial benefits of proactively identifying and mitigating risks through ESI.
- Consider potential losses avoided by addressing security vulnerabilities and ethical concerns.
- Project ROI is based on the reduction of financial risks associated with unforeseen issues.
-
Long-Term Sustainability:
- Assess the financial value of creating a sustainable and responsible organizational culture.
- Consider the potential for long-term cost savings related to ethical and secure practices.
- Project ROI is based on the contribution of ESI to the organization's resilience and longevity.
When calculating ROI in the context of ESI, it's essential to consider both tangible and intangible benefits. ESI's impact on avoiding potential damages and fostering a positive organizational culture contributes significantly to the overall return on investment.
In summary, the expected ROI accompanying the harmonious confluence of AI, Organizational Development, and ESI is multifaceted. From operational efficiency gains to enhanced security savings, increased innovation potential to elevated employee satisfaction, the amalgamation of these frameworks promises measurable returns on the initial investment. As organizations embark on this transformative journey, the ROI becomes not only a financial metric but a testament to the enduring value derived from the strategic integration of AI, OD, and ESI.
Written by Joseph Raynus
Our team of industry thought leaders are always engaged with researching, sharing thought leadership, publishing, and representing our firm in the industry. In addition to their published works, you can find digital assets that reinforce similar topics, and offer various ways to experience the content.
Join the ranks of leading organizations that have partnered with AMS to drive innovation, improve performance, and achieve sustainable success. Let’s transform together, your journey to excellence starts here.